ABB is currently investigating cloud computing and big data technologies in the context of power and automation. Cloud computing is already common for customer relationship management systems or human resource management systems, but industrial automation is still in the process of moving to the cloud. As an early example, ABB’s SCADA system for oil&gas applications, SCADAvantage, can now be purchased as hosted version in a GlobaLogix data center.
Big data processing amongst other things involves crossing structured and unstructured data to create new insights for customers. Unstructured data can for example be video streams or social media output. ABB’s Asset Health Center is one of the first solutions for processing big data for smart grids. ABB is executing several research projects on cloud computing and big data, providing great opportunities for scientific and industrial research beyond the buzzwords. We are hiring PhD-level professionals!

Category Archives: ABB
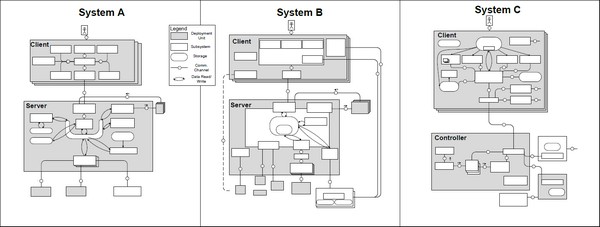
Experiences from Identifying Software Reuse Opportunities by Domain Analysis
We got a paper accepted at the Industry Track of the 17th International Software Product Line Conference (SPLC2013) to be held August 26th-30th in Tokyo, Japan: In the paper, we describe how we applied existing domain analysis approaches for software product line engineering and tailored them to include a feature analysis as well as architecture evaluation. We report our experiences from applying the approach in two subdomains of industrial automation.
ABB among MIT's 50 disruptive companies in 2013
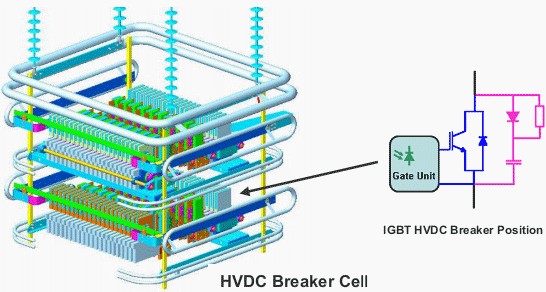
ABB’s breakthrough developing an HVDC circuit breaker now led to an inclusion to MIT Technology Review’s list of 50 disruptive companies 2013 along with companies such as Apple, SpaceX, and Facebook. The HVDC breaker enables building direct current grids, whereas before only point-to-point lines were possible. This may lead to widespread use of renewable energy.
Why ABB is a software company
The latest issue of ABB’s corporate technical journal “ABB Review” features the theme “Software”. With around 3,000 software developers in 40 countries worldwide and impacting about one quarter of ABB’s revenue, there is no doubt that ABB is a major software company. The theme issue provides an overview on some of ABB’s latest activites for embedded, system, and enterprise software as well as software processes. Check out how we prepare our controllers for the multi-core challenge and how we use performance modelling to plan the capacity and software architectures of our back-end IT.
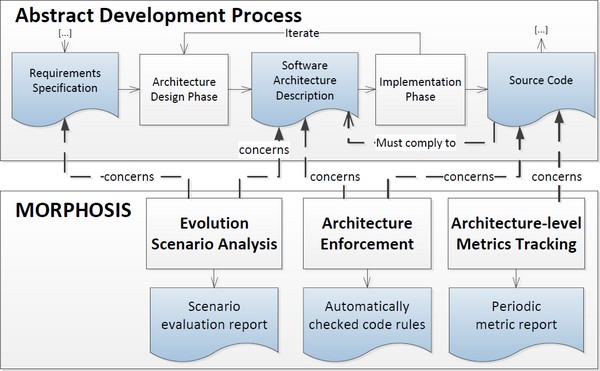
MORPHOSIS: A Case Study on Lightweight Architecture Sustainability Analysis
Here are the slides from my talk at WICSA 2012:
MORPHOSIS: A Lightweight Method Facilitating Sustainable Software Architectures
A new paper was accepted for a working session at WICSA 2012 in Helsinki: “Managing the cost-effective evolution of industrial software systems is a challenging task because of their complexity and long lifetimes. We have applied several recent sustainability evaluation and improvement approaches to the software architecture of a large industrial software system from ABB. We combined our selection of approaches in a lightweight method called MORPHOSIS“.
ICPE 2012 Best Industry-Related Paper Award
Our paper “An industrial case study of performance and cost design space exploration” has won an ICPE 2012 Best Paper Award. It describes how PerOpteryx was applied for design space exploration on a web-based system from ABB.
ABB Robot serving Wheat Beer
Nice, looks really professional. Cheers!
Zooming Process Graphics
Looks neat: ABB HawkEye is a research prototype of a new operator interface for process control. HawkEye is developed by ABB Strategic R&D for Oil, Gas & Petrochemicals.
IEEE names ABB technologies among the 11 most important of the decade
Along with smartphones and digital photography, FACTS has been named among the top 11 technologies of the decade by the IEEE. The 11 technologies named in the list include smartphones, social networking, voice over IP, LED lighting, cloud computing, multicore CPUs, digital photography, drone aircraft, class-D audio and planetary rovers. FACTS (flexible AC transmission systems) also finds a place in this illustrious list. FACTS is a family of technologies that ABB pioneered and has continuously developed over the past 60 years.
“With these technologies ABB can increase the capacity of existing lines by as much as 50 percent, reduce electrical losses in long distance power transfer and relieve grid congestion and transmission bottlenecks that prevent the flow of electricity,” said Ingela Hålling, head of FACTS within the Grid Systems business of the Power Systems division. “FACTS technologies can also help to minimize the risk of blackouts, and facilitate the integration of intermittent types of energy by rapidly countering voltage fluctuations or by storing large amounts of surplus power until it is needed.”
ABB has delivered around 800 FACTS installations worldwide, which is more than half the world total.